In recent years, the Australian labour hire industry has repeatedly faced accusations of substandard workplace health and safety practices, as well as worker exploitation. Issues such as wage theft, denial of worker rights, and company phoenixing are usually at the top of the list when the discussion remerges.
In order to combat these shadier parts of the labour hire sector, the governments of Queensland, Victoria and South Australia have all enacted their respective labour hire licensing laws. Other regions are discussing similar action, and there are hints of a federal-level scheme across the whole of Australia.
Labour hire licensing acts work to protect Australian workers from exploitation, whether that’s in the form of unlawful work standards or unethical practices more generally. If you provide workers to a host organization in any of the above regions, you are legally required to have a labour hire licence.
What is a Labour Hire Licence?
Under the labour hire work model, there are three parties at play. A worker, a labour hire company and a host organization. Workers (labour) are directly employed by the labour hire company, which then allocate the labour to the host organizations that need them.
Generally speaking, a licence is a form of certification needed in order to undertake a certain business activity. A labour hire licence, then, is essentially a means of verifying that a labour hire company is in compliance with employment regulations. Labour hire licences protect workers from exploitation because all the other parties involved must operate more transparently.
Who Needs a Labour Hire Licence?
Any business in Queensland, Victoria or South Australia that provides labour hire services must now be licensed. The Victorian Labour Hire Licencing Authority defines a labour hire provider as:
An individual or organisation that, in the course of conducting a business, has an arrangement with one or more individuals under which the business supplies the individuals to perform work in and as part of a host’s business or undertaking.
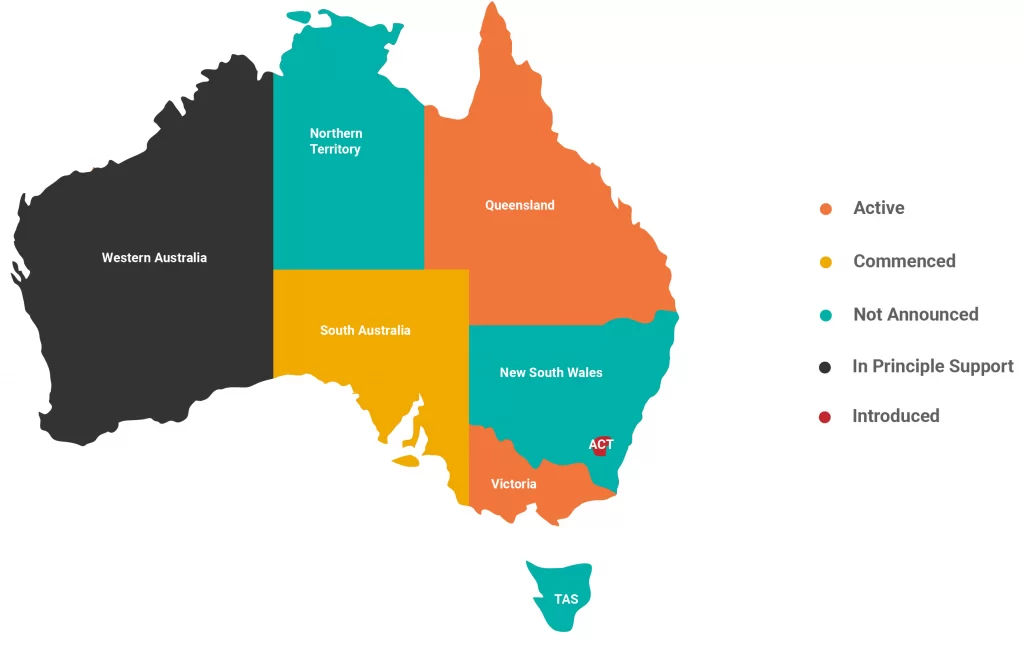
Labour hire licencing acts were brought into effect in Queensland and South Australia in 2017, and Victoria in 2018. Equivalent schemes are pending in Australian Capital Territory, and under discussion in Western Australia. In New South Wales, Northern Territory and Tasmania, there are currently no schemes announced.
Which Businesses must have Labour Hire Licences?
Any business that supplies workers to another individual or organisation must abide by the labour hire licensing scheme of their region. A worker is generally defined as an individual who has an arrangement with the labour provider, under which they are supplied to a third party. Recruitment and permanent placement services, volunteering and workplace consultancy are not considered labour hire services.
Here are some common examples of businesses that must have labour hire licences:
- A contractor who supplies workers to a farmer to pick produce.
- An employment agency who on-hires temporary staff to a business.
- An IT recruitment service that supplies a business with additional IT workers.
- A security company that provides a business with security staff for crowd control.
Queensland labour hire licensing guidelines give examples of the wide range of industries affected by these licencing schemes, including nursing, horticulture, construction, security, consultancy traffic management, and food processing. Any labour hire provider who supplies temporary workers in these common instances (and indeed many others) will require a labour hire licence.
What happens if a Business is Unlicensed?
Labour hire providers in the regions of Queensland, Victoria and South Australia are legally required to apply for a licence. Companies that host workers also have a legal responsibility to ensure the labour hire company they work with is fully licenced. Fines of over $500,000 can apply to host businesses that hire workers from unlicensed labour hire providers.
It’s essential for host businesses to ensure they’re only involved with reputable labour hire providers that hold the licence required to supply workers. If you don’t know whether or not you require a labour hire licence, it’s best to consult state regulations or get in touch with a trusted labour hire company for advice.